In most applications, one cell is rarely enough to enable optimal capacity. Battery manufacturers must apply physical theories to production, including installing batteries in parallel and series.
Depending on the circuit, the output varies to cater to specific needs. Then what is the difference? Scroll down to learn the answer.
Wiring Batteries In Series: Pros & Cons
Connecting two or more batteries in a series diagram means attaching the positive terminal of one to the negative terminal of the next. The purpose of this move is to increase the overall circuit voltage without changing the ampere-hours.
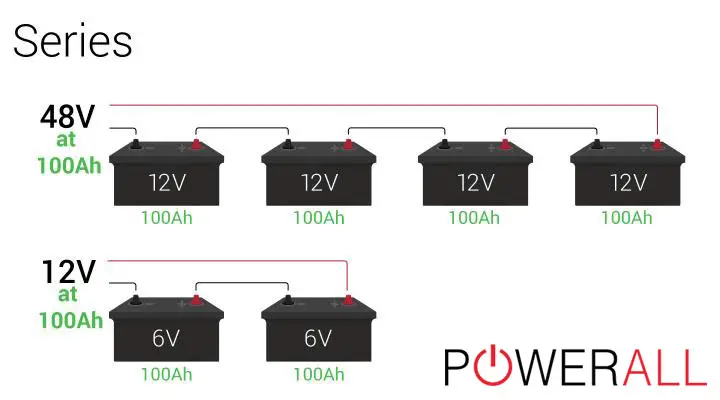
Suppose you set up two 12V – 26Ah cells in series. The system then records the combined voltage of 24 volts and amp loads of 26Ah. When you add one more source, the total batteries in the series will reach up to 36 volts.
The participating components must have the same voltage level and rating to implement this model. For example, you cannot wire a 12V – 20Ah to a 6V – 10Ah. The charge rate should take place evenly to maintain optimal performance. Or, at the very least, you should add a charge controller that supplies extra power to the system.
Pros
The basic law of physics confirmed: In the same power system, the higher the voltage, the lower the load current. For instance, a 1200W device operating at 12V consumes 100A and 25A at 48V.
It’s easy to see that users benefit from thinner wiring (due to less current load). The series configuration reduces costs compared to that of a single battery.
In addition, the bank of batteries becomes more stable because the voltage drop rarely interrupts the overall operation. This is also why electrical equipment often requires a high-power supply. The same principle also applies to charging systems.
Cons
The biggest disadvantage of a series-connected circuit is that the effective voltage output is established. Simply put, all devices in this scheme only function at the higher voltage. All items compatible with the lower level will fail to connect to the system unless you install a converter.
This setup may become a nightmare once one of the batteries fails. It causes a sudden voltage drop that stops or damages existing equipment if you do not take precautions.
Batteries In Parallel: Pros & Cons
A parallel bank consists of two or more batteries connected by the same terminal – positive terminals together and negative ones together. As a result, the amp load increases, but the voltage remains unchanged.
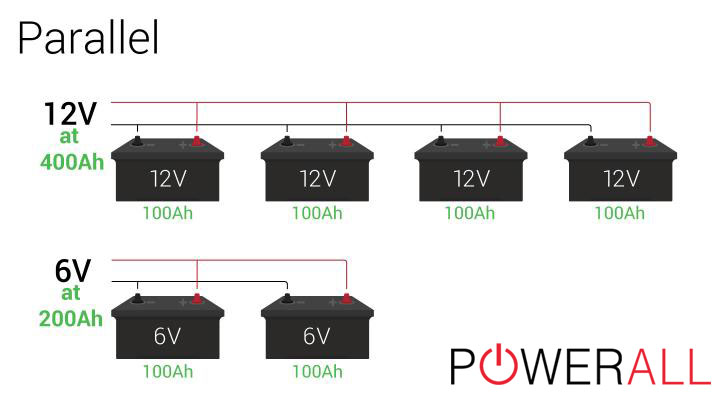
For instance, when two 12V – 100Ah cells join in the parallel pattern, you will get a battery system that functions at 12V – 200Ah. Once another similar cell appears, the current reaches 300 amp/hour of energy.
Similar to the series connection method, synchronization between the cells is required. This parallel battery bank, on the other hand, only requires the same voltage. A link between 6V and 24V batteries is not possible.
Pros
If you go for parallel wiring, you get a longer duration. The reason is that increased amp-hour capacity develops proportionally to the number of batteries in the system. The runtime doubles when you have two items.
Another advantage of battery setup in parallel is protection for other components in case of any battery failure. Once an individual source is broken, it does not affect the entire system. The working products continue to power your device.
Cons
What was a benefit of a series connection of batteries is now a disadvantage of parallel configuration. The higher current rating, compared to that of the series wiring, resulting in thicker cables.
You may also face frequent energy drops and less efficient appliance operation. Besides, the higher amp capacity prolongs the charge time.
Wiring Batteries In Series Vs. Parallel: Which Is Better?
A Quick Comparison
Efficiency
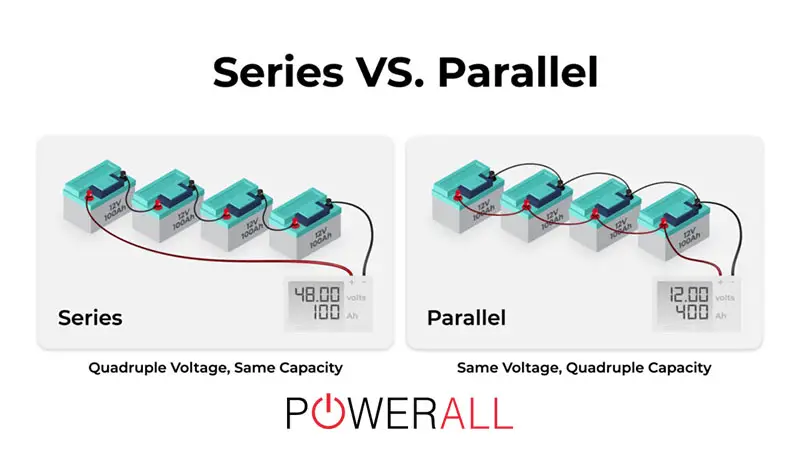
It is clear from the two sections above that the main difference between wiring batteries in the two methods is their output voltage and current load.
Though the total energy does not change, the voltage increases and the amp draw decreases for series wiring and vice versa. However, it is not all of the comparisons!
Durability
Batteries in parallel have a long usage period due to the same operating mechanism in terms of type, age, and size. Despite similar cell requirements in the series type, some cells may experience uneven discharge.
This leads to small differences that build up over time, increasing the risk of damage. Meanwhile, all batteries in parallel can run with a decreasing voltage and an equal discharge rate.
Power
Another win goes to the parallel wiring when it comes to power. Each device benefits from the full voltage in this network instead of receiving only half the power. Suppose you install two energy-consuming devices. They operate at optimal levels thanks to an abundant supply.
Safety
On the user’s vehicle, neither is more secure. What matters here is the supply voltage in total. If this reading rises above 30 volts, it becomes dangerous because it exceeds the natural tolerance of the human body.
Moving to other components in the circuit, parallel wiring seems more reliable when problems occur. The appliance and even healthy batteries have their pathway, thus staying safe from electricity failure.
Verdict
Although the parallel wiring may appear superior in the comparison, it does not necessarily outperform in all cases. The optimal choice depends on the needs of the device you use.
For conventional accessories or vehicles such as boats or recreational vehicles, parallel sets of batteries are the simplest and most effective solution that meets the power needs.
However, for huge electric motors or solar setups that require more than 3000 watts of power, taking advantage of wiring batteries in series is the best idea. The higher battery voltage increases the efficiency of the volt motor and minimizes energy loss.
How To Connect Batteries In Series And Parallel
Before going through our step-by-step instructions below, say no to mix and match. All cells, regardless of type of battery chemistry, must share the same features.
Tutorial For Parallel Wiring
- Connect the negative cable (-) of the first battery to the negative terminal of the second battery. Do the same with the remaining batteries in the system, if any.
- Attach the positive (+) terminal of the first battery to the positive terminal of the next one. Perform similar actions for the rest.
- Connect the positive terminal of the last component in the circuit to the positive terminal of the power unit. Repeat with the negative terminals.
Tutorial For Series Wiring
- Connect the negative cable of one battery to a positive termnial of another.
- Apply this principle to all remaining cells until they connect straight. You now have two unused ends – the first battery’s positive terminal and the last battery’s negative terminal.
- Connect the last positive end to the negative end of the power unit and do the same thing with the remaining negative ones.
Can I Use Batteries In Series And Parallel At The Same Time?
Yes, of course, but the series-parallel configuration is not as interlaced as you might think. Instead, you install in sets to get a large battery bank that produces greater operating voltage and capacity.
Say, you have 6 cells of 6V – 100Ah. Place them into two parallel columns, with each having 3 cells. In each row, you must arrange them in a setting so that there is no similar terminal close to each other, and 3 rows are the same. It should be like this:
(Negative-positive) and (negative-positive)
(Negative-positive) and (negative-positive)
(Negative-positive) and (negative-positive)
Or vice versa.
Then, connect the three negative/positive terminals of three cells together on each outer side – parallel wiring. On the inner side, link the positive terminal of this cell to the negative terminal of the opposite one – series wiring. You will end up with a 6-cell battery delivering 12V and 300Ah.
The general principle of the series-parallel connection is the same as for the single battery. If you are not confident in your technique, consult a professional.
FAQs
How Many Batteries Can You Wire In Series?
The exact amount depends on the brands of batteries. For example, Aolithium allows two lithium batteries for one of its models to generate a larger pack of 24V. Meanwhile, the 4S models can form 4 series batteries.
How Many 12 Volt Batteries Can You Run In Parallel?
Check with the manufacturer for the answer. However, you can expect up to 4 batteries in a circuit.
Do Batteries In Parallel Drain Equally?
Definitely, yes. Parallel battery packs balance automatically after a period. As a result, equal charge is also achieved among the joint cells as long as the link between the terminals is still there. Hence, the batteries drain at the same time.
Do Batteries In Parallel Need Balancing?
No, it is not necessary for batteries consisting of more than one cell. On the other hand, doing so even reduces the cycle life and battery capacity.
Conclusion
A general rule of the correct method is to use cells with similar specifications. Otherwise, you inevitably suffer from wiring batteries in parallel danger, such as overheating, leak, or explosion. Take this precaution into consideration when it comes to series configuration too. For the rest of the operations, you can complete it in a flash if you follow our instructions.








0 Comments